Upgrade¶
With a library as experienced as GeoTools you will occasionally run into a project from ten years ago that needs to be upgraded. This page collects the upgrade notes for each release change; highlighting any fundamental changes with code examples showing how to upgrade your code.
The first step to upgrade: change the geotools.version of your dependencies in your pom.xml to 34.0:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<geotools.version>34.0</geotools.version>
</properties>
....
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-bom</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-shapefile</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-swing</artifactId>
</dependency>
....
</dependencies>
GeoTools 34.x¶
Maven Bill of Materials¶
GeoTools has adopted the use of Maven Bill of Materials (BOM) to advertise both the versions of GeoTools modules and the third party libraries used by GeoTools.
This change will significantly reduce the amount of work expected of downstream projects, however to take advantage of this you will need to perform some clean up of your pom.xml
to remove dependencies, and especially remove version numbers.
Use maven import scope to include the gt-bom:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-bom</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
GeoTools dependencies can then be listed without version numbers:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-shapefile</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-swing</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
To align third party dependencies with those used by GeoTools import the gt-platform-dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-platform-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
Third-party dependences such as the postgresql jdbc driver can then be listed without version numbers:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
</dependency>
Java 17 Minimum¶
GeoTools 34.x is the first series requiring Java 17 minimum.
Javas 17 introduces additional Java Runtime Environment protections “Strongly Encapsulate JDK Internals” and “Sealed Classes”. These new restrictions have resulted in several significant component upgrades (ImageN and removal of JAI Tools) outlined below.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<release>17</release>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Migration to Eclipse ImageN¶
The Eclipse ImageN library is continuing the work of Java Advanced Imaging thanks to a code donation from Oracle. In order to provide test coverage the project has directly incorporated the JAI-Ext operators and improvements that have been made on behalf of the GeoTools and GeoServer projects.
Migration instructions and script are provided by the new ImageN project:
ImageN is available as individual maven modules, or as a combined imagen-all module.
BEFORE:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.media</groupId>
<artifactId>jai_core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
</dependency>
import javax.media.jai.JAI;
import javax.media.jai.RenderedOp;
import com.sun.media.jai.codec.FileSeekableStream;
import javax.media.jai.widget.ScrollingImagePanel;
AFTER:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.imagen</groupId>
<artifactId>imagen-core</artifactId>
<!-- version managed via gt-platform-dependencies bom -->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.imagen</groupId>
<artifactId>affine</artifactId>
<!-- version managed via gt-platform-dependencies bom -->
</dependency>
import org.eclipse.imagen.JAI;
import org.eclipse.imagen.RenderedOp;
import org.eclipse.imagen.media.codec.FileSeekableStream;
import org.eclipse.imagen.widget.ScrollingImagePanel;
GeoTools ImageN API Changes¶
Additional GeoTools migration guidance:
JAIExt utility class is no longer required and has been removed.
Logging has been updated,
Logging.IMAGENis now used to configure ImageN loggingTHe constant ImageMosaicFormat.USE_JAI_IMAGEREAD has changed to ImageMosaicFormat.USE_IMAGEN_IMAGEREAD.
ComponentColorModelJAI: Deprecated, no longer required, maintained for serialization compatibility
Removal of JAI Tools¶
To facilitate the migration to Eclipse ImageN the JAI Tools library is no longer available.
GeoTools now uses equivalent functionality:
Use of RangeLookupTable and Range
In the case of statistics has internally adopted JAI Tools code
BEFORE:
import org.jaitools.numeric.Range;
import org.jaitools.media.jai.rangelookup.RangeLookupTable;
Range<Double> span = Range.create(0.0,true,5.0,false);
Range<Float> span1 = Range.create(0.0f,true,10.0f,false);
Range<Float> span2 = Range.create(10.0f,true,null,true);
RangeLookupTable lookup = CoverageUtilities.getRangeLookupTable(List.of(span1,span2),-1.0f);
PolygonExtractionProcess.process(band,insideEdges,noDataValues,List.of(span1,span2));
JAI-Ext:
import it.geosolutions.jaiext.range.Range;
import it.geosolutions.jaiext.range.RangeFactory;
import it.geosolutions.jaiext.rlookup.RangeLookupTable;
RangeDouble span1 = (RangeDouble) RangeFactory.create(0.0,true,5.0,false);
RangeFloat span1 = (RangeFloat) RangeFactory.create(0.0f,true,10.0f,false);
RangeFloat span2 = (RangeFloat) RangeFactory.create(10.0f,true,null,true);
RangeLookupTable lookup = CoverageUtilities.getRangeLookupTable(List.of(span1,span2),-1.0f);
PolygonExtractionProcess.process(band,insideEdges,noDataValues,List.of(span1,span2));
ImageN:
import org.eclipse.imagen.media.range.Range;
import org.eclipse.imagen.media.rangerange.RangeFactory;
import org.eclipse.imagen.media.rlookup.RangeLookupTable;
RangeDouble span = RangeFactory.create(0.0,true,5.0,false);
RangeFloat span1 = RangeFactory.create(0.0f,true,10.0f,false);
RangeFloat span2 = RangeFactory.create(10.0f,true,null,true);
RangeLookupTable lookup = CoverageUtilities.getRangeLookupTable(List.of(span1,span2),-1.0f);
PolygonExtractionProcess.process(band,insideEdges,noDataValues,List.of(span1,span2));
GeoTools 32.x¶
End Java 11 Compatibility¶
GeoTools 32.x is the final release compatible with Java 11.
ImageMosaic Deserialization Validation¶
Since GeoTools 31.4, class names are validated when deserializing sample image files for ImageMosaic.
If the default allowlist of classes that image mosaic will deserialize is preventing the usage of valid
sample image files, the org.geotools.gce.imagemosaic.sampleimage.allowlist system property can be set to
allow additional classes whose fully-qualified class names match the provided regular expression.
Since GeoTools 32.3, certain fields of the javax.media.jai.remote.SerializableRenderedImage class are
blocked by the default allow list to block deserializing instances of that class. GeoTools has migrated to
the using the org.geotools.gce.imagemosaic.SampleImage class since version 16.2 (released February 2017)
so most users will probably not be affected by this but the following example shows how to set the system
property to allow SerializableRenderedImage instances if necessary:
org.geotools.gce.imagemosaic.sampleimage.allowlist=^java\\.(net\\.InetAddress|util\\.Hashtable)$
JDBC Method signature change in PreparedStatementSQLDialect¶
The method PreparedStatementSQLDialect.setValue(Object, Class<?>, PreparedStatement, int, Connection) was refactored to receive an additional argument.
The new signature is PreparedStatementSQLDialect.setValue(Object, Class<?>, AttributeDescriptor, PreparedStatement, int, Connection).
The AttributeDescriptor passed corresponds to the feature’s attribute and maybe be null in cases where no attribute is directly available.
From now on, the sqlType for a specific feature attribute is taken into consideration for INSERT and UPDATE operations, rather than solely the attribute’s class. The type is now determined by the new method org.geotools.jdbc.JDBCDataStore.getMapping(Class<?>, AttributeDescriptor): Integer.
Users of JDBCDataStore are not affected. Custom implementations of org.geotools.jdbc.PreparedStatementSQLDialect must be adjusted to the new method signature in order to compile.
NetCDF Version upgrade to 5.5.3¶
GeoTools 32.0 upgraded underlying Unidata NetCDF libraries from 4.6.15 to 5.5.3 which includes internal GRIB mapping table updates and GRIB parameters interpretation updates. The upgrade impacted the way the GRIB parameters are being retrieved as well the way the temporal information is being extracted from the underlying data which may affect the construction of the names and the reported temporal ranges as well, resulting in some breakage with the upgrade.
Refer to GEOT-7547 for relevant details on what has been broken.
If a GRIB dataset stopped working:
Remove any auxiliary/cache file associated with the underlying GRIB file (assuming the file is named gribfile.grib2):
gribfile.ncx3
gribfile.ncx4
gribfile.gbx9
.gribfile_hash folder (if not previously deleted) located beside the original file.
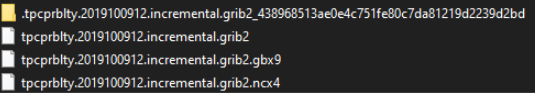
The screenshot below, represents an actual example of a tpcprblty.2019100912.incremental.grib2 file with related auxiliary/cache files
Additional steps needed in case of ImageMosaic of GRIBs¶
Remove any automatically created ImageMosaic configuration file within the ImageMosaic root folder. Assuming the underlying ImageMosaic was named mosaicM, containing coverages related to VariableA, VariableB, VariableC, …:
VariableA.properties, VariableB.properties, VariableC.properties, …
VariableAsample_image.dat, VariableBsample_image.dat, VariableCsample_image.dat, …
mosaicM.xml
If using a datastore.properties connecting to an actual DB, cleanup the tables from the DB
Assuming that all the grib files belonging to the same ImageMosaic are affected by the same issue, you can delete the related tables and allow the imageMosaic reconfiguration to recreate them.
Based on the above example, the naming convention is that granules for VariableA are stored on table named VariableA and so on.
Recreate the indexer.xml and _auxiliary.xml file as reported in the NetCDF documentation . (At the end, GRIB file are served through the NetCDF libraries)
GeoTools 31.x¶
DataStore Optimization uses Actual Query¶
The actual query can now be passed to the method to determine whether the DataStore implementation can optimize for specific queries.
For example, canLimit() changes to canLimit(query) so the actual query can be evaluated and used to determine the response of true or false. Previously, canLimit() had to respond in a generic way, without the benefit of the query. The old methods have been deprecated.
This allows some simple queries to be optimized when possible without also having to optimize for more complex queries (which might not be possible for the particular DataStore.)
For more details on whether a method can be optimized in this way, please refer to the API docs and the tutorial.
GeoTools 30.x¶
This update contains a major breaking change to the GeoTools library refactoring to remove the org.opengis pacakage.
The gt-opengis module has been renamed, change your dependency to:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-api</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
Unfortunately we could not maintain a deprecation cycle for this change and have provided an update script to assist.
Remove OpenGIS and Cleanup GeoTools API¶
The package org.opengis has changed org.geotools.api.
To aid in this transition an Apache Ant script is provided:
Download Ant script
remove-opengis.xmlincluded with this documentation.The default
updatetarget will update your Java code andMETA-INF/services:Use the absolute path for project.dir:
ant -f remove-opengis.xml -Dproject.dir=(absolute path to your project directory)
Or copy
remove-opengis.xmlfile into your project directory and run:ant -f remove-opengis.xml
We have done our best to with this update script but it is not perfect - known issues:
Double check use of geometry Position and temporal Position which have the same classname in different packages
Clean up unused or duplicate imports
You may need to re-run code formatters
Data API¶
The main data access interfaces have been moved from org.geotools.data to org.geotools.api.data.
This includes, DataStore, FeatureSource, FeatureIterator, and many others.
As part of the move, the datastore registration files found in META-INF/services need to be moved as well,
in particular:
org.geotools.data.DataAccessFactory
org.geotools.data.DataStoreFactorySpi
org.geotools.data.FileDataStoreFactorySpi
should now be named:
org.geotools.api.data.DataAccessFactory
org.geotools.api.data.DataStoreFactorySpi
org.geotools.api.data.FileDataStoreFactorySpi
The upgrade script should take care of this change.
ISO Geometry¶
The org.opengis.geometry interfaces (for Point, Curve and Surface and supporting classes) were no longer in use.
The direct use of JTS Topology Suite Geometry is now used throughout the library. Previously Object was used
requiring a cast to Geometry.
// cast to Geometry no longer needed
Geometry geometry = feature.getDefaultGeometry();
DirectPosition and GeneralEnvelope cleanup¶
The org.opengis.geometry and org.opengis.geometry.coordinates interfaces for positions, envelopes and bounding boxes have been revised as part of their refactor to org.geotools.api.
GeoAPI Preflight / OpenGIS |
GeoTools 30.x API |
|---|---|
org.opengis.geometry.BoundingBox |
org.geotools.api.geometry.BoundingBox |
org.opengis.geometry.BoundingBox3D |
org.geotools.api.geometry.BoundingBox3D |
org.opengis.geometry.DirectPosition |
org.geotools.api.geometry.Position |
org.opengis.geometry.Envelope |
org.geotools.api.geometry.Bounds |
org.opengis.geometry.coordinates.PointArray |
java.util.List<Position> |
org.opengis.geometry.coordinates.Position |
org.geotools.api.geometry.Position |
GeoTools 29.x Implementation |
GeoTools 30.x Implementation |
|---|---|
org.geotools.geometry.AbstractDirectPosition |
org.geotools.api.geometry.AbstractPosition |
org.geotools.geometry.AbstractEnvelope |
org.geotools.api.geometry.AbstractBounds |
org.geotools.geometry.DirectPosition1D |
org.geotools.api.geometry.Position1D |
org.geotools.geometry.DirectPosition2D |
org.geotools.api.geometry.Position2D |
org.geotools.geometry.DirectPosition3D |
org.geotools.api.geometry.Position3D |
org.geotools.geometry.Envelope2D |
org.geotools.geometry.jts.ReferencedEnvelope |
org.geotools.geometry.GeneralDirectPosition |
org.geotools.api.geometry.GeneralPosition |
org.geotools.geometry.GeneralEnvelope |
org.geotools.api.geometry.GeneralBounds |
For the most part these changes are method compatible, attempting common replacements:
Replace
ReferencedEnvelope.create(Envelope,CoordinateReferenceSystem)withReferencedEnvelope.envelope(Envelope,CoordinateReferenceSystem)Replace constructor
Envelope2D(crs,x,y,width,height)withReferencedEnvelope.rect(x,y,width,height,crs)Replace
Envelope2D.equals(Envelope2D)withReferencedEnvelope.boundsEquals2D(Bounds,double)Replace
Envelopefield accessx,``y``,``width``,``height`` with appropriate methods (exampleReferencedEnvelope.getMinX())
GeoTools 29.x¶
Java 17 as the minimum version¶
GeoTools 34.x requires Java 17 as the minimum version. If you are still using Java 11, you will have to remain on GeoTools 33.x or earlier.
Deprecated functions removed¶
In gt-wfs-ng we’ve removed:
org.geotools.data.wfs.WFSFeatureReader.WFSFeatureReader(GetParser<SimpleFeature>)
GeoTools 27.x¶
Log4JLoggingFactory migrated to Reload4J¶
We have changed to testing Log4JLoggingFactory against reload4j project.
The Log4J 1.2 API has been retired from Apache, and the API is now maintained by the Reload4J project:
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.reload4j</groupId>
<artifactId>reload4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.19</version>
</dependency>
We encourage applications to use Reload4J, or migrated to a supported logging library.
Logging and GeoTools.init()¶
Previously GeoTools.init() would prefer which prefer CommonsLoggerFactory if the commons-logging API was available on the CLASSPATH.
The GeoTools.init() changed to determine appropriate logger using the following precedence:
org.geotools.util.logging.LogbackLoggerFactory- SLF4J APIorg.geotools.util.logging.Log4j2LoggerFactory- Log4J 2 APIorg.geotools.util.logging.Log4j1LoggerFactory- Log4J 1.2 API (maintained by Reload4J project)org.geotools.util.logging.CommonsLoggerFactory- Apache’s Common Logging framework (JCL API)No factory selected, makes direct use of Java Util Logging API (configured with )
The method confirms the required API is available on the CLASSPATH before selecting a LoggerFactory. If the required API is not-available the next LoggerFactory is tried.
To use GeoTools.init():
package net.fun.example;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import org.geotools.util.factory.GeoTools;
import org.geotools.util.logging.Logging;
class Example {
public static void main(String args[]){
GeoTools.init();
Logger LOGGER = Logging.getLogger("org.geotools.tutorial");
LOGGER.fine("Application started - first post!")
}
}
In a production environment several logging libraries from different components may be available. To select a specific LoggingFactory use GeoTools.setLoggingFactory(LoggingFactory):
package net.fun.example;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import org.geotools.util.factory.GeoTools;
import org.geotools.util.logging.Logging;
class Example {
public static Logger LOG = defaultLogger();
public static void main(String args[]){
LOGGER.fine("Application started - first post!")
}
private static final Logger defaultLogger(){
GeoTools.setLoggerFactory(Log4JLoggerFactory.getInstance());
return Logging.getLogger(Example.class);
}
}
For more information see LoggerFactory.
GeoTools 26.x¶
Shapefile¶
ShapefileDataStore will autodetect DBF charset from CPG sidecar file, the feature now enabled by default. When this feature is enabled, the following rules apply:
if no explicit charset parameter passed to
ShapefileDataStoreFactory, it will instruct createdShapefileDataStoreto try and figure out DBF file charset from CPG file. In this case, CPG files must contain correct charset name, otherwise, these files should be removed, or updated properly.if the store fails to read CPG, it uses the default charset specified by
ShapefileDataStoreFactory.DBFCHARSETconstant, which is usual behavior.
In case of trouble there is an ability to bring old behavior back by setting org.geotools.shapefile.enableCPG system property
to “false”. This turns autodetection off. The name of the property stored in ShapefileDataStoreFactory.ENABLE_CPG_SWITCH constant.
Unit of Measurement Formatting¶
As more third-party libraries adopt the Java module system, stricter rules regarding access to non-public parts of other modules apply.
One such case was the way GeoTools’ unit formatters were previously initialized, which caused GeoTools to fail immediately when run from the module path.
Fixing this required changes to multiple classes:
GeoToolsUnitFormatwhich was previously used to access innards of a third-party library and provide access to GeoTools-specific unit formatting instance has been split up and moved: * Building and initializing individual unit formatting instances can now be done using theorg.geotools.measure.BaseUnitFormatterconstructor (instead of extendingorg.geotools.util.GeoToolsUnitFormatand its inner classBaseGT2Format). * The GeoTools-specific formatting instance can now be accessed withorg.geotools.measure.UnitFormat.getInstance()(instead oforg.geotools.util.GeoToolsUnitFormat.getInstance()).org.geotools.referencing.wkt.DefaultUnitParserhas been moved and renamed toorg.geotools.measure.WktUnitFormat.
Improvements to Regex Parsing in IsLike and similar filters¶
Processing of regular expressions in the IsLike & StrMatches functions, and in the isPropertyLike
filter to make use of the faster and more robust Google regular expression’s library. As part of this work we have improved the handling of some “permissible”
but inadvisable patterns, such as those with multi character escapes or wild cards. If you had patterns that
relied on long escape or wild card patterns you may now get an IllegalArgumentException for a pattern that
happened to work in the past.
GeoTools 25.x¶
GeoTools¶
In GeoTools 25.7 GeoTools.getInitialContext().look(name) and related methods have been deprecated, with GeoTools.jndiLookup(name). We have also taken an opportunity to remove GeoTools.fixName( context, name )
The use of GeoTools.jndiLookup(name) is subject to validation with the default GeoTools.DEFAULT_JNDI_VALIDATOR validator used limit name lookup.
BEFORE
context = GeoTools.getInitialContext();
String fixedName = GeoTools.fixName( context, name );
return (DataSource) context.lookup(fixedName);
AFTER
return (DataSource) GeoTools.jndiLookup(name);
More variable arguments support in core classes¶
Several code classes have been switched to use varargs instead of explicit arrays.
While the old clients are compatible with these changes, there’s now an opportunity
to simplify code.
BEFORE
// style creation
FeatureTypeStyle fts = styleFactory.createFeatureTypeStyle(new Rule[] {rule});
// query handling
Query q = new Query(tname("ft1"));
q.setSortBy(new SortBy[] {new SortByImpl("prop", ASCENDING)});
q.setPropertyNames(new String[] {"geom"});
// feature building
SimpleFeatureBuilder fb = new SimpleFeatureBuilder(targetType);
SimpleFeature = fb.buildFeature("f1", new Object[] {null, 1}));
// test collection creation
SimpleFeatureCollection collection = DataUtilities.collection(new SimpleFeature[] {feature1, feature2});
AFTER
// style creation
FeatureTypeStyle fts = styleFactory.createFeatureTypeStyle(rule);
// query handling
Query q = new Query(tname("ft1"));
q.setSortBy(new SortByImpl("prop", ASCENDING));
q.setPropertyNames("geom");
// feature building
SimpleFeatureBuilder fb = new SimpleFeatureBuilder(targetType);
SimpleFeature = fb.buildFeature("f1", null, 1));
// test collection creation
SimpleFeatureCollection collection = DataUtilities.collection(feature1, feature2);
DataStore creation parameters¶
The DataAccess and DataStore creation parameters have been switched from Map<String, Serializable>
to Map<String, ?>, to match actual usage (some stores require non serializable parameters).
This should not affect end users of the API, but DataAccessFactory and DataStoreFactory
implementations will have to be updated to match.
For those feeding Properties object to DataAccess.getDataStore() a new utility method,
DataUtilities.toConnectionParameters has been made available, which converts a Properties
to a Map<String, ?>.
Map<String,?> connectionParameters = DataUtilities.toConnectionParameters(properties);
DataStore dataStore = DataStoreFinder.getDataStore(connectionParameters);
HTTPClient moved to its own module¶
A new module gt-http has been established for the HTTPClient API.
The original interfaces HTTPClient and HTTPResponse and their implementations:
(SimpleHttpClient, DelegateHTTPClient, LoggingHTTPClient and DelegateHTTPResponse) have moved from
org.geotools.data.ows to the org.geotools.http package.
Placeholders for the previous implementations remain in place, with a deprecation reminding you to switch to the new import as out outlined in the table below.
Deprecated class |
Module |
Replacement (other module) |
|---|---|---|
org.geotools.data.ows.AbstractHttpClient |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.AbstractHttpClient |
org.geotools.data.ows.MockHttpClient |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.MockHttpClient |
org.geotools.data.ows.MockHttpResponse |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.MockHttpResponse |
org.geotools.data.ows.DelegateHTTPClient |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.DelegateHTTPClient |
org.geotools.data.ows.DelegateHTTPResponse |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.DelegateHTTPResponse |
org.geotools.data.ows.HTTPClient |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.HTTPClient |
org.geotools.data.ows.HTTPResponse |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.HTTPResponse |
org.geotools.data.ows.LoggingHTTPClient |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.LoggingHTTPClient |
org.geotools.data.ows.SimpleHttpClient |
gt-main |
org.geotools.http.SimpleHttpClient |
org.geotools.ows.wms.MultithreadedHttpClient |
gt-wms |
org.geotools.http.MultithreadedHttpClient (gt-http-commons) |
org.geotools.ows.MockHttpClient |
gt-wms |
org.geotools.http.MockHttpClient |
org.geotools.ows.MockHttpResponse |
gt-wms |
org.geotools.http.MockHttpResponse |
org.geotools.ows.wmts.MockHttpClient |
gt-wmts |
org.geotools.http.AbstractHttpClient |
org.geotools.data.mongodb.MockHTTPClient |
gt-mongodb |
org.geotools.http.MockHttpClient |
org.geotools.data.mongodb.MockHttpResponse |
gt-mongodb |
org.geotools.http.MockHttpResponse |
org.geotools.ows.wfs.MultithreadedHttpClient |
gt-wfs-ng |
org.geotools.http.MultithreadedHttpClient (gt-http-commons) |
org.geotools.ows.wfs.AbstractTestHTTPClient |
gt-wfs-ng |
org.geotools.http.AbstractHttpClient |
org.geotools.data.Base64 |
gt-main |
org.geotools.util.Base64 (gt-metadata) |
This will result in a compile error in cases where GeoTools returns org.geotools.http.HTTPClient.
BEFORE (compile error):
import org.geotools.ows.HTTPClient;
WebMapServer wms = new WebMapServer("http://atlas.gc.ca/cgi-bin/atlaswms_en?VERSION=1.1.1&Request=GetCapabilities&Service=WMS");
HTTPClient client = wms.getHTTPClient();
AFTER change imports (recommended):
import org.geotools.http.HTTPClient;
WebMapServer wms = new WebMapServer("http://atlas.gc.ca/cgi-bin/atlaswms_en?VERSION=1.1.1&Request=GetCapabilities&Service=WMS");
HTTPClient client = (HTTPClient) wms.getHTTPClient();
ALTERNATIVE add cast (continue to use deprecated api):
import org.geotools.data.ows.HTTPClient;
WebMapServer wms = new WebMapServer("http://atlas.gc.ca/cgi-bin/atlaswms_en?VERSION=1.1.1&Request=GetCapabilities&Service=WMS");
HTTPClient client = (HTTPClient) wms.getHTTPClient();
HTTPClientFinder¶
To allow the library to be configured with different HTTPClient implementations HTTPClientFinder is recommend:
BEFORE:
import org.geotools.data.ows.HTTPClient;
import org.geotools.data.ows.HTTPResponse;
import org.geotools.ows.SimpleHttpClient;
HTTPClient http = new SimpleHttpClient();
HTTPResponse response = http.get();
AFTER:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-http</artifactId>
<version>${gt.version}</version>
</dependency>
import org.geotools.http.HTTPClient;
import org.geotools.http.HTTPResponse;
import org.geotools.http.HTTPClientFinder;
HTTPClient http = HTTPClientFinder.createClient();
HTTPResponse response = http.get();
In addition a new plugin gt-http-commons has been added for MultithreadedHttpClient.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-http-commons</artifactId>
<version>${gt.version}</version>
</dependency>
import org.geotools.http.HTTPClient;
import org.geotools.http.HTTPResponse;
import org.geotools.http.HTTPClientFinder;
import org.geotools.http.commons.MultihreadedHttpClient;
Hints hints = new Hints(Hints.HTTP_CLIENT, MultihreadedHttpClient.class);
HTTPClient http = HTTPClientFinder.createClient(hints);
HTTPResponse response = http.get();
WMTS - WebMapTileServer initialisation¶
We have introduced a new contructor for the WebMapTileServer. The reason is that any HTTP headers must be specified prior to initialisation.
This might introduce a problem where a constuctor taking three arguments are used.
See list of available constructors:
public WebMapTileServer(URL serverURL, HTTPClient httpClient)
public WebMapTileServer(URL serverURL, HTTPClient httpClient, Map<String, String> headers) // <- NEW CONSTRUCTOR
public WebMapTileServer(URL serverURL, HTTPClient httpClient, WMTSCapabilities capabilities)
public WebMapTileServer(URL serverURL, HTTPClient httpClient, WMTSCapabilities capabilities, Map<String, Object> hints)
For the same reason we will not allow changes to the headers after initialisation,
and have deprecated public Map<String, String> getHeaders().
GeoTools 24.x¶
The Oracle extension was upgraded to use the current JDBC driver release. If you are using oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver in your code to load the JDBC driver you should change this to oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver.
DbaseFileHeader.readHeader(ReadableByteChannel, Charset) method was removed. Instead DbaseFileHeader constructor must be used to pass a charset and DbaseFileHeader.readHeader(ReadableByteChannel) to read the header.
The Units library (JSR 385) was updated to Units 2.0. This is mostly a change from package tec.uom.se.* to tech.units.indriya.*. If you make any use of the Units library in your own code you will need to update the imports. There are also changes to the arithmetic operations’ names. See this blog post for more details.
GeoTools 22.x¶
Change to repo.osgeo.org for GeoTools releases¶
Use osgeo repository https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/release/:
Replaces osgeo release repository
http://download.osgeo.org/webdav/geotools/for GeoTools releases.This is a group repository used by several OSGeo projects.
This group repository also provides third-party dependencies used by GeoTools (such as JTS and JAI-EXT).
BEFORE pom.xml:
<repository>
<id>osgeo</id>
<name>Open Source Geospatial Foundation Repository</name>
<url>http://download.osgeo.org/webdav/geotools/</url>
</repository>
AFTER pom.xml:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>osgeo</id>
<name>OSGeo Release Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/release/</url>
<snapshots><enabled>false</enabled></snapshots>
<releases><enabled>true</enabled></releases>
</repository>
</repositories>
Alternative: Mirror retired repo.boundlessgeo.com¶
To build existing projects referencing http://repo.boundlessgeo.com/, with no modifications to pom.xml, configure mirrors using ~/.m2/settings.xml.
Change to settings.xml:
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>osgeo-release</id>
<name>OSGeo Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/release/</url>
<mirrorOf>osgeo</mirrorOf> <!-- previously http://download.osgeo.org/webdav/geotools/ -->
</mirror>
<mirror>
<id>geoserver-releases</id>
<name>Boundless Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/Geoserver-releases/</url>
<mirrorOf>boundless</mirrorOf> <!-- previously http://repo.boundlessgeo.com/main/ -->
</mirror>
</mirrors>
Both of the above repositories above are included in https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/release/ group repository. The mirror settings are intended as a temporary measure to allow your projects to build while you update your pom.xml to use the osgeo release repository.
Change to repo.osgeo.org for GeoTools snapshots¶
Use osgeo-snapshots repository https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/snapshot/:
Replaces boundless snapshot repository
http://repo.boundlessgeo.com/mainfor the GeoTools SNAPSHOTS.This is a group snapshot repository used by several OSGeo projects
The contents of the boundless repository https://repo.boundlessgeo.com/main/ previously included snapshots of active GeoTools builds. The repository https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/geotools-snapshots/ has taking over this role for the GeoTools project ( and is included in the group repository https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/snapshot/).
To update existing projects making use of an active branch replace boundless snapshot repository with osgeo-snapshot repository.
BEFORE pom.xml:
<repository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>boundless</id>
<name>Boundless Maven Repository</name>
<url>http://repo.boundlessgeo.com/main</url>
</repository>
AFTER pom.xml:
<repository>
<id>osgeo-snapshot</id>
<name>OSGeo Snapshot Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/snapshot/</url>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled></snapshots>
<releases><enabled>false</enabled></releases>
</repository>
GeoTools 21.x¶
GeoTools 21 is the first release compatible with Java 8 and Java 11.
Restructured Library¶
The library has been restructured with automatic module names for Java 11 use.
The following table shows how maven dependencies have changed, and the resulting automatic module name for Java 11 use.
Dependency |
Upgrade |
Automatic Module Name |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(removed) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repackage Library¶
Previously GeoTools reused packages across modules by design, this approach is no longer supported by JDK resulting in the following classes changing package.
Module |
Package |
|---|---|
Upgrade |
Package |
Classes Affected |
|
|
|
|
|
Abstract Store, Wrapper |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AbstractDecorator, Wrapper |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Upgrading projects using historical GeoTools snapshots¶
The contents of the boundless repository https://repo.boundlessgeo.com/main/ previously included snapshots of active GeoTools builds. The repository https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/geotools-snapshots/ has taking over this role for the GeoTools project ( and is included in the group repository https://repo.osgeo.org/repository/snapshot/).
The geotools-snapshots is populated from active branches only and does not contain “historical” snapshots from prior releases. Due to this limitation we recommend upgrading historical projects to the appropriate GeoTools release.
As an example to fix an existing project build using GeoTools 21-SNAPSHOT which is no longer available upgrade to the most recent 21.x series release.
BEFORE pom.xml:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<geotools.version>21-SNAPSHOT</geotools.version>
</properties>
AFTER pom.xml:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<geotools.version>21.5</geotools.version>
</properties>
GeoTools 20.x¶
GeoTools 20 requires Java 8.
Upgrade to JTS-1.16¶
The transitive dependency will correctly bring in the required jars:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.locationtech.jts</groupId>
<artifactId>jts-core</artifactId>
<version>${jts.version}</version>
</dependency>
Package change to org.locationtech.jts
This release changes the package names from com.vividsolutions.jts to org.locationtech.jts. To update your own code follow the JTS Upgrade Guide instructions.
Using the command line to update your own pom.xml files:
git grep -l com.vividsolutions | grep pom.xml | xargs sed -i "s/com.vividsolutions/org.locationtech.jts/g"
And codebase:
git grep -l com.vividsolutions | xargs sed -i "s/com.vividsolutions/org.locationtech/"
Use of copy rather than clone
If you are in the habit of using clone to duplicate JTS objects (such as Geometry and Coordinate) you will find the clone method has been deprecated, and a copy method introduced to explicitly perform a deep copy:
Geometry duplicate = geom.copy();
Migrate to JSR-363 Units¶
This releases upgrades from the unofficial JSR-275 units library to the official JSR-363 units API.
Maven transitive dependency will correctly bring in the required jars:
<dependency>
<groupId>systems.uom</groupId>
<artifactId>systems-common-java8</artifactId>
<version>0.7.2</version>
</dependency>
Package names have changed, resulting in some common search and replaces when upgrading:
Search
javax.measure.unit.Unitreplacejavax.measure.UnitSearch
ConversionExceptionreplaceIncommensurableExceptionThis is a checked exception, in areas of the GeoTools library where this was found we now return an
IllegalArgumentexception.Search
converter == UnitConverter.IDENTITYreplaceconverter.isIdentity()Search
javax.measure.unit.NonSIreplaceimport si.uom.NonSISearch
javax.measure.unit.SIreplaceimport si.uom.SISearch
SI.METERreplaceSI.METRESearch
javax.measure.converter.UnitConverterreplacejavax.measure.UnitConverterSearch
javax.measure.unit.UnitFormatreplaceimport javax.measure.format.UnitFormatSearch
Unit.ONEreplaceAbstractUnit.ONESearch
Dimensionless.UNITreplaceAbstractUnit.ONESearch
Unit.valueOf(unitString)replaceUnits.parseUnit(unitString)
Getting Unit instances
If you know the unit to use at compile time, use one of the Unit instances defined as static variables in org.geotools.measure.Units, si.uom.SI, si.uom.NonSI or systems.uom.common.USCustomary.
If you need to define new Units at runtime, it is important to immediately try to convert the new unit to one of the existing instances using Units.autocorrect method. Autocorrect applies some tolerance to locate an equivalent Unit. Skipping autocorrect will produce unexpected results and errors due to small differences in units definition.
// the result should be NonSI.DEGREE_ANGLE:
Unit<?> deg = Units.autoCorrect(SI.RADIAN.multiply(0.0174532925199433));
Unit<?> halfMetre = SI.METRE.divide(2);
// the result should be SI.METRE
Unit<?> unit = Units.autocorrect(halfMetre.multiply(4).divide(2));
public <T extends Quantity<T>> Unit<T> deriveUnit(Unit<T> baseUnit, double factor) {
return Units.autocorrect(baseUnit.multiply(factor);)
}
Use a specific Quantity whenever possible
This allows for type-safety checks at compile time:
Unit<Length> halfMetre = SI.METRE.divide(2);
Unit<Length> stupidUnit = Units.autocorrect(halfMetre.multiply(4).divide(2));
Formatting units
Use org.geotools.measure.Units.toName(unit) to get the unit name (or unit label if name is not defined).
Unit<?> unit = ...
System.out.println(Units.toName(unit)):
Use org.geotools.measure.Units.getDefaultFormat().format() to get the unit label (ignoring the name).
// prints "Litre"
System.out.println(Units.toName(SI.LITRE))
// prints "l"
System.out.println(Units.getDefaultFormat().format(SI.LITRE))
// Most units don't define a name, so it does not make a difference
// prints "m"
System.out.println(Units.toName(SI.METRE))
// prints "m"
System.out.println(Units.getDefaultFormat().format(SI.METRE))
Converting units
If the unit Quantity type is known, use the type-safe getConverterTo() method:
Unit<Angle> unit = ...
UnitConverter converter = unit.getConverterTo(SI.RADIAN);
double convertedQuantity = converter.convert(3.1415);
If the Quantity type is undefined, use the convenience method org.geotools.measure.Units.getConverterToAny(). Note that this method throws an IllegalArgumentException if units can’t be converted:
Unit<?> unit = ...
UnitConverter converter = Units.getConverterToAny(unit, SI.RADIAN);
double convertedQuantity = converter.convert(3.1415);
Using units
If previously you made use of the Units in your code, to help with unit conversion or simply to keep the units straight. You might have code like:
Measure<Double, Length> dist = Measure.valueOf(distance, SI.METER);
System.out.println(dist.doubleValue(SI.KILOMETER) + " Km");
System.out.println(dist.doubleValue(NonSI.MILE) + " miles");
You will find it no longer compiles. It should be converted to use the Quantity classes.
import javax.measure.Quantity;
import javax.measure.quantity.Length;
import si.uom.SI;
import systems.uom.common.USCustomary;
import tec.uom.se.quantity.Quantities;
import tec.uom.se.unit.MetricPrefix;
Quantity<Length> dist = Quantities.getQuantity(distance, SI.METRE);
System.out.println(dist.to(MetricPrefix.KILO(SI.METRE)).getValue() + " Km");
System.out.println(dist.to(USCustomary.MILE) + " miles");
GeoTools 19.x¶
GeoTools is built and tested with Java 8 at this time, to use this library in a Java 9 or Java 10 environment additional JVM runtime arguments are required:
--add-modules=java.xml.bind --add-modules=java.activation -XX:+IgnoreUnrecognizedVMOptions
These settings turn on several JRE modules that have been disabled by default in Java 9 onward.
GeoTools 15.x¶
GeoTools 15.x requires Java 8:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<inherited>true</inherited>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
GeoTools 14.x¶
From 14.x version, the JAI-EXT Project has been integrated in GeoTools. This project provides a high scalable Java API for image processing with support for NoData and ROI.
This integration provides also the removal of the following classes, since they are now inside JAI-EXT:
ColorIndexerfrom gt-coverage module;GTCropfrom gt-coverage module;GenericPiecewisefrom gt-render module;RasterClassifierfrom gt-render module;ArtifactsFilterfrom gt-imagemosaic module.
Users may now decide to choose between JAI and JAI-EXT operations by simply using the JAIExt class containing utility methods for handling JAI/JAI-EXT registration.
A more detailed tutorial on how to use JAI-EXT may be found at the following JAI-EXT Tutorial Page.
TextSymbolizer provides direct access to the device independent Font list, removing deprecated array access methods. This change restores SLD 1.0 multi-lingual behavior allowing several face/size combinations to be used during labeling.
BEFORE:
textSymbolizer.addFont(font);
Font[] array = textSymbolizer.getFonts();
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++){
Font f = textSymbolizer.getFonts()[i];
...
}
AFTER:
textSymbolizer.fonts().add(font);
for(Font f : textSymbolizer.fonts()){
...
}
Transaction is now Closable for use with try-with-resource syntax:
try (Transaction t = new DefaultTransaction()){
store.setTransaction( t );
store.addFeatures( newFeatures );
t.commit();
}
ShapefileDataStore representing shapefiles without any data, now return empty bounds on getBounds() instead of the bounds inside the shapefile header (mostly [0:0,0:0]). So bounds.isEmpty() and bounds.isNull() will return true for empty shapefiles.
GeoTools 13.0¶
As of GeoTools 13.0, the CoverageViewType classes have been removed. The AbstractDataStore class is also now deprecated. Extensive work has been done to bring in ContentDataStore as its replacement.
There is a ContentDataStore Tutorial to help with migration from AbstractDataStore.
Many readers and iterators are now Closable for use with try-with-resource syntax:
try( SimpleFeatureIterator features = source.getFeatures( filter ) ){
while( features.hasNext() ){
SimpleFeature feature = features.next();
...
}
}
GeoTools 12.0¶
GeoTools now requires Java 7 and this is the first release tested with OpenJDK! Please ensure you are using JDK 1.7 or newer for GeoTools 12. Both Oracle Java 7 and OpenJDK 7 are supported, tested, release targets.
Filter interfaces have been simplified. The GeoTools interfaces have been deprecated since GeoTools 2.3, and finally they have been removed. All filter interfaces now use the GeoAPI Filter.
GeoTools 11.0¶
Only new features were added in GeoTools 11.0.
GeoTools 10.0¶
GeoTools 10 add significant improvements in the coverage reading API.
For those migrating the first visible benefit is that referring to a generic grid coverage reader does not require anymore to use AbstractGridCoverage2DReader (an abstract class) but to the new GridCoverage2DReader interface. The old usage is still supported though, as most readers are still extending the same base class, but the usage of the interface allows for reader wrappers.
BEFORE:
AbstractGridCoverage2DReader reader = format.getReader(source);
AFTER:
GridCoverage2DReader reader = format.getReader(source);
GeoTools 9.0¶
GeoTools 9 has resolved a long standing conflict between FeatureCollection acting as a “result” set capable of
streaming large data sets vs. acting as a familiar Java Collection. The Java 5 “for each” syntax prevents
the safe use of Iterator (as we cannot ensure it will be closed). As a result FeatureCollection no longer
can extend java Collection and is acting as a pure “result set” with streaming access provided by FeatureIterator.
ReferencedEnvelope and CRS¶
ReferencedEnvelope has in the past only supported 2D extents, we have introduced the subclass ReferencedEnvelope3D
to support CoordinateReferenceSystems with three dimensions.
There is now a new factory method to safely construct the appropriate implementation for a provided CoordinateReferenceSystem
as shown below.
BEFORE:
ReferencedEnvelope bbox = new ReferencedEnvelope( crs );
ReferencedEnvelope copy = new ReferencedEnvelope( bbox );
AFTER:
ReferencedEnvelope bbox = ReferencedEnvelope.create( crs );
ReferencedEnvelope copy = ReferencedEnvelope.create( bbox );
This represents an incompatible API change, existing code using new ReferencedEnvelope may now throw
a RuntimeException when supplied with an incompatible CoordinateReferenceSystem.
FeatureCollection Add¶
With the FeatureCollection.add method being removed, you will need to use an explicit instance that supports
adding content.
BEFORE:
SimpleFeatureCollection features = FeatureCollections.newCollection();
for( SimpleFeature feature : list ){
features.add( feature );
}
AFTER:
DefaultFeatureCollection features = new DefaultFeatureCollection();
for( SimpleFeature feature : list ){
features.add( feature );
}
ALTERNATE (will throw exception if FeatureCollection does not implement
java.util.Collection):
Collection<SimpleFeature> collection = DataUtilities.collectionCast( featureCollection );
collection.addAll( list );
ALTERNATE DETAIL:
SimpleFeatureCollection features = FeatureCollections.newCollection();
if( features instanceof Collection ){
Collection<SimpleFeature> collection = (Collection) features;
collection.addAll( list );
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("FeatureCollections configured with immutbale implementation");
}
SPECIFIC:
ListFeatureCollection features = new ListFeatureCollection( schema, list );
FeatureCollection Iterator¶
The deprecated FeatureCollection.iterator() method is no longer available, please use FeatureCollection.features()
as shown below.
BEFORE:
Iterator i=featureCollection.iterator();
try {
while( i.hasNext(); ){
SimpleFeature feature = i.next();
...
}
}
finally {
featureCollection.close( i );
}
AFTER:
FeatureIterator i=featureCollection.features();
try {
while( i.hasNext(); ){
SimpleFeature feature = i.next();
...
}
}
finally {
i.close();
}
JAVA7:
try ( FeatureIterator i=featureCollection.features()){
while( i.hasNext() ){
SimpleFeature feature = i.next();
...
}
}
How to Close an Iterator¶
We have made FeatureIterator implement Closable (for Java 7 try-with-resource compatibility). This
also provides an excellent replacement for
FeatureCollection.close(Iterator).
If you are using any wrapping Iterators that still require the ability to close()
please consider the following approach.
BEFORE:
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
try {
...
} finally {
if (collection instanceof SimpleFeatureCollection) {
((SimpleFeatureCollection) collection).close(iterator);
}
}
QUICK:
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
try {
...
} finally {
DataUtilities.close( iterator );
}
DETAIL:
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
try {
...
} finally {
if (iterator instanceof Closeable) {
try {
((Closeable)iterator).close();
}
catch( IOException e){
Logger log = Logger.getLogger( collection.getClass().getPackage().toString() );
log.log(Level.FINE, e.getMessage(), e );
}
}
}
JAVA7 using try-with-resource syntax for Iterator that implements Closeable:
try ( Iterator i=collection.features()){
while( i.hasNext() ){
Object object = i.next();
...
}
}
GeoTools 8.0¶
The changes moving from GeoTools 2.7 to GeoTools 8.0 have a great emphasis on usability and documentation. Because of the focus on ease of use; many of the changes here are marked “Optional” this indicates that your code will not break; but you have a chance to clean it up and make your code more readable.
Style¶
Some of the gt-opengis style methods that have been deprecated for a while are now removed.
Mark.getRotation()/Mark.setRotation( Expression )Mark.getSize()/Mark.setSize( Expression )
These are handled in a similar manner:
BEFORE:
for( GraphicalSymbol symbol : graphic.graphicalSymbols() ){ if( symbol instanceof Mark ){ Mark mark = (Mark) symbol; mark.setSize( ff.literal( 8 ) ); } }
AFTER:
graphic.setSize( ff.literal( 8 ) );
Filter¶
The filter system was upgrade to match Filter 2.0 resulting in a few additions. This mostly effects people writing their own functions (as now we need to know about parameter types).
FeatureId¶
BEFORE:
FilterFactory2 ff = CommonFactoryFinder.getFilterFactory2(null); Filter filter; Set<FeatureId> selected = new HashSet<FeatureId>(); selected.add(ff.featureId("CITY.98734597823459687235")); selected.add(ff.featureId("CITY.98734592345235823474")); filter = ff.id(selected);
AFTER
FilterFactory ff = CommonFactoryFinder.getFilterFactory(); Filter filter = ff.id(ff.featureId("CITY.98734597823459687235"), ff.featureId("CITY.98734592345235823474"));
Function¶
We have extended gt-opengis Function to make the FunctionName description (especially
argument names) more available.
To update your code:
class SplitFunction implements Function { public static FunctionName NAME = new FunctionNameImpl( "split", "geometry", "line" ); ... FunctionName getFunctionName(){ return NAME; } ... }
If you are extending abstract function expression base class; it provides a default implementation
of getFunctionName() allowing your code to compile.
FunctionExpression¶
In a related matter gt-main no longer provides access to the deprecated FunctionExpression
interface (it has returned an empty set for several releases now):
BEFORE:
Set<String> proposals = new TreeSet<String>(); Set<Function> oldFunctions = FunctionFinder. CommonFactoryFinder.getFunctionExpressions(null); for( Function function : oldFunctions ) { proposals.add(function.getName().toLowerCase()); }
AFTER:
Set<String> proposals = new TreeSet<String>(); FunctionFinder functionFinder = new FunctionFinder(null); for( FunctionName function : functionFinder.getAllFunctionDescriptions() ){ proposals.add(function.getName().toLowerCase()); }
Direct Position and Envelope¶
Deprecated methods in gt-opengis and gt-referencing have now been removed.
Deprecated method in 2.7 |
Replacement in 8.0 |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
|
For consistency with ISO 19107 |
|
|
For consistency with ISO 19107 |
|
|
For consistency with ISO 19107 |
|
|
Remove duplication |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For consistency with ISO 19107 |
|
|
For consistency with ISO 19107 |
NumberRange¶
The gt-metadata NumberRange class is finally shedding some of its deprecated methods.
BEFORE:
NumberRange before = new NumberRange( 0.0, 5.0 );
AFTER:
NumberRange<Double> after1 = new NumberRange( Double.class, 0.0, 5.0 );
NumberRange<Double> after2 = NumberRage.create( 0.0, 5.0 );
GeoTools 2.7¶
The changes from GeoTools 2.6 to GeoTools 2.7 focus on making your code more readable; you will
find a number of optional changes (such as using Query rather than DefaultQuery) which will
simplify make your code easier to follow.
Query¶
The gt-api module has been updated to make Query a concrete class rather than an interface.
BEFORE:
Query query = new DefaultQuery( typeName, filter );
AFTER:
Query query = new Query( typeName, filter );
Tips:
You can perform a search and replace to change
DefaultQuerytoQueryon your code baseIf you have your own implementation of
Queryyour code is now broken; after many years we have never seen an implementation ofQueryin the wild. You should be able to fix by extending rather then implementingQuery.DefaultQuerystill exists but all of the implementation code has now been “pulled up” intoQueryandDefaultQuerymarked as deprecated.In a similar fashion
FeatureLockcan now be directly constructed rather than use aFactory.
SimpleFeatureCollection¶
We have vastly cut down the use of Java generics for casual users of the GeoTools library. The
primary example of this is the introduction of SimpleFeatureCollection (which saves you
typing in FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> each time).
BEFORE:
FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> source = (FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>) dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName ); Query query = new DefaultQuery( typeName, filter ); FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> featureCollection = source.getFeatures( query );
AFTER:
SimpleFeatureSource source = dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName ); Query query = new Query( typeName, filter ); SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection = source.getFeatures( query );
Tips:
You can do a search and replace on this one; but you need to be very careful with any implementations you have that accept a
FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>as a method parameter!Be careful if you have your own
FeatureStoreimplementation; a search and replace will change several of your methods so they no longer “override” the default implementation provided byAbstractFeatureStore.:@Override // this would fail; you do use Override right? public Set addFeatures( SimpleFeatureCollection features ){ ... your implementation goes here ...To fix this code you will need to “undo” your search and replace for this method parameter:
@Override public Set addFeatures( FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> features ){ ... your implementation goes here ...
Note: If you use the
@Overrideannotation in your code you will get a proper error; since your new method would no longer override anything.
SimpleFeatureSource¶
The gt-api module now defines SimpleFeatuyreSource (to save you a bit of typing). In addition
the DataStore interface now returns a SimpleFeatureSource; so if you want you optionally
can update your code for readability.
BEFORE:
FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> source = (FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>) dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName );
AFTER:
SimpleFeatureSource source = dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName );
Tips:
* you can do this with a search and replace
* Be a bit careful when you have one of your own methods that is expecting a FeatureSource
SimpleFeatureStore¶
In a similar fashion returns a SimpleFeatureCollection; it also has a couple of its own tricks:
BEFORE:
FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> source = (FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>) dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName ); if( source instanceof FeatureStore){ // read write access FeatureStore<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> store = (FeatureStore<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>) source; store.addFeatures( newFeatures ); ...
AFTER:
SimpleFeatureSource source = dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName ); if( source instanceof SimpleFeatureStore){ // read write access SimpleFeatureStore store = (SimpleFeatureStore) source; store.addFeatures( newFeatures ); ...
SimpleFeatureLocking¶
You can also explicitly use SimpleFeatureLocking if you want read/write/lock access to simple
feature content. Much like Query it has been made a concrete class.
FeatureStore modifyFeatures by Name¶
The FeatureStore method modifyFeatures now allows you to modify features by name.
BEFORE:
FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> source = (FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>) dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName ); if( source instanceof FeatureStore){ // read write access FeatureStore<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> store = (FeatureStore<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>) source; SimpleFeatureType schema = store.getSchema(); AttributeDescriptor attribute = schema.getDescriptor( attributeName ); store.modifyFeatures( attribute, attributeValue, filter );
AFTER:
SimpleFeatureSource source = dataStore.getFeatureSource( typeName ); if( source instanceof SimpleFeatureStore){ // read write access SimpleFeatureStore store = (SimpleFeatureStore) source; store.modifyFeatures( attributeName, attributeValue, filter ); ...
Tips:
Generic
FeatureSourceallowsmodifyFeatures(Name, Value, filter)
CoverageProcessor¶
The DefaultProcessor and AbstractProcessor classes have been merged into a single class called
CoverageProcessor.
BEFORE:
final DefaultProcessor processor= new DefaultProcessor(hints)
AFTER:
final CoverageProcessor processor= new CoverageProcessor(hints)
Or better:
final CoverageProcessor processor= CoverageProcessor.getInstace(hints);
Tips:
Try to always use the static
getDefaultInstancemethod in order to leverage onSoftReferencecaching
GeneralEnvelope¶
We have been removing old deprecated code from the GeneralEnvelope class.
Old Method |
New Method |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GeoTools 2.6¶
The GeoTools 2.6.0 release is incremental in nature with the main change being the introduction
of the JDBC-NG DataStores the idea of Query capabilities (so you can check what hints are
supported).
GridRange Removed¶
GridRange implementations have been removed as the result of a change we are inheriting from GeoAPI
where a switch from GridRange to GridEnvelope has been made. GridRange comes from
Grid Coverages Implementation specification 1.0 (which is basically dead) while
GridEnvelope comes from ISO 19123 which looks like the replacement.
There is a big difference between interfaces though:
GridRangetreats its own maximum grid coordinates as EXCLUSIVE (like Java2D classesRectangle2D,RenderedImageandRasterdo); whileGridEnvelopeuses a different convention where maximum grid coordinates are INCLUSIVE.
This is shown in the code example below with the maxx variable.
As far as switching over to the new classes, the equivalence are as follows:
Replace
GridRange2DwithGridGeneralBoundsNotice that now
GridGeneralBoundsis a Java2DRectangleand that it is also mutable!Replace
GeneralGridRangewithGeneralGridEnvelope
There are a few more caveats, which we are showing here below.
BEFORE:
Use
getSpanwheregetLengthwas usedBe EXTREMELY careful with the conventions for the inclusion/exclusion of the maximum coordinates.
GridRange2DIS aRectangleand is mutable now!BEFORE:
import org.geotools.coverage.grid.GeneralGridRange; final Rectangle actualDim = new Rectangle(0, 0, hrWidth, hrHeight); final GeneralGridRange originalGridRange = new GeneralGridRange(actualDim); final int w = originalGridRange.getLength(0); final int maxx = originalGridRange.getUpper(0); ... import org.geotools.coverage.grid.GridRange2D; final Rectangle actualDim = new Rectangle(0, 0, hrWidth, hrHeight); final GridRange2D originalGridRange2D = new GridRange2D(actualDim); final int w = originalGridRange2D.getLength(0); final int maxx = originalGridRange2D.getUpper(0); final Rectangle rect = (Rectangle)originalGridRange2D.clone(); {code}
AFTER:
import org.geotools.coverage.grid.GeneralGridEnvelope; final Rectangle actualDim = new Rectangle(0, 0, hrWidth, hrHeight); final GeneralGridEnvelope originalGridRange=new GeneralGridEnvelope (actualDim,2); final int w = originalGridRange.getSpan(0); final int maxx = originalGridRange.getHigh(0)+1; import org.geotools.coverage.grid.GridGeneralBounds; final Rectangle actualDim = new Rectangle(0, 0, hrWidth, hrHeight); final GridGeneralBounds originalGridRange2D = new GridGeneralBounds(actualDim); final int w = originalGridRange2D.getSpan(0); final int maxx = originalGridRange2D.getHigh(0)+1; final Rectangle rect = (Rectangle)originalGridRange2D.clone();
OverviewPolicy Enum replace Hint use¶
The hints to control overviews were deprecated and have now been removed.
The current deprecated values have been remove from the Hints class inside the Metadata module:
VALUE_OVERVIEW_POLICY_QUALITYIGNORE_COVERAGE_OVERVIEWVALUE_OVERVIEW_POLICY_IGNOREVALUE_OVERVIEW_POLICY_NEARESTVALUE_OVERVIEW_POLICY_SPEED
You should use the Enum that comes with the OverviewPolicy Enum. Here below you will find a few examples:
BEFORE:
Hints hints = new Hints(); hints.put(Hints.OVERVIEW_POLICY, Hints.VALUE_OVERVIEW_POLICY_SPEED); WorldImageReader wiReader = new WorldImageReader(file, hints);
AFTER:
Hints hints = new Hints(); hints.put(Hints.OVERVIEW_POLICY, OverviewPolicy.SPEED); WorldImageReader wiReader = new WorldImageReader(file, hints);
Hints:
Please, notice that the
OverviewPolicyEnumprovides a method to get the default policy for overviews. The method isgetDefaultPolicy().
CoverageUtilities and FeatureUtilities¶
Deprecated methods have been remove from coverage utilities classes;
We have removed deprecated methods from classes:
CoverageUtilities.javaFeatureUtilities.java
Existing code should change as follows:
BEFORE:
final FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> fc=FeatureUtilities.wrapGridCoverageReader(reader)
AFTER:
final GeneralParameterValue[] params=... final FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> fc=FeatureUtilities.wrapGridCoverageReader(reader,params)
Hints:
This change allows us to store basic parameters to control how we will perform subsequent reads from this reader. The
AbstractGridFormatREAD_GRIDGEOMETRY2Dparameter will be always overridden during a subsequent read.
Coverage Processing Classes¶
Deprecated methods have been remove from coverage processing classes:
filteredSubsample(GridCoverage, int, int, float[], Interpolation, BorderExtender)has been removed
Here is what that looks like in code:
BEFORE:
public GridCoverage filteredSubsample(final GridCoverage source, final int scaleX, final int scaleY, final float\[\] qsFilter, final Interpolation interpolation, final BorderExtender be) throws CoverageProcessingException { return filteredSubsample(source, scaleX, scaleY, qsFilter, interpolation); }
AFTER:
public GridCoverage filteredSubsample(final GridCoverage source, final int scaleX, final int scaleY, final float\[\] qsFilter, final Interpolation interpolation){ // recolor(GridCoverage, Map\[\]) has been removed ... }
BEFORE:
recolor(final GridCoverage source, final Map[] colorMaps)
AFTER:
recolor(final GridCoverage source, final ColorMap[] colorMaps); // scale(GridCoverage, double, double, double, double, Interpolation, BorderExtender) has been removed
BEFORE:
scale(GridCoverage, double, double, double, double, Interpolation, BorderExtender)
AFTER:
scale(GridCoverage,double,double,double,double,Interpolation) // scale(GridCoverage, double, double, double, double, Interpolation, BorderExtender) has been removedBEFORE:
BEFORE:
scale(GridCoverage, double, double, double, double, Interpolation, BorderExtender)
AFTER:
scale(GridCoverage,double,double,double,double,Interpolation)
DefaultParameterDescriptor and Parameter¶
Removed deprecated constructors from DefaultParameterDescriptor and Parameter classes.
BEFORE:
DefaultParameterDescriptor(Map<String,?>,defaultValue,minimum, maximum, unit, required) DefaultParameterDescriptor(Map<String,?>, defaultValue, minimum, maximum, required) DefaultParameterDescriptor(name, defaultValue, minimum, maximum) DefaultParameterDescriptor(name, defaultValue, minimum, maximum, unit) DefaultParameterDescriptor(name, remarks, defaultValue, required) DefaultParameterDescriptor(name, defaultValue) DefaultParameterDescriptor( name, valueClass, defaultValue) Parameter(name, value) Parameter(name, value, unit) Parameter(name, value)
AFTER:
DefaultParameterDescriptor.create(...) Parameter.create(...)
GeoTools 2.5¶
The GeoTools 2.5.0 release is a major change to the GeoTools library due to the adoption of both Java 5 and a new feature model.
FeatureCollction¶
In transitioning your code to Java 5 please be careful not use use the for each loop construct.
We still need to call FeatureCollection.close( iterator).
Due to this restriction (of not using for each loop construct we have had to make FeatureCollection
no longer Collection.
Example (GeoTools 2.5 code):
FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> featureCollection = feaureSource.getFeatures(); Iterator<SimpleFeature> iterator = featureCollection.iterator(); try { while( iterator.hasNext() ){ SimpleFeature feature = iterator.next(); ... } } finally { featureCollection.close( iterator ); }
Example (GeoTools 2.7 code)
We have removed the need for the use of generics to minimize typing:
SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection = feaureSource.getFeatures(); SimpleFeatureIterator iterator = featureCollection.features(); try { while( iterator.hasNext() ){ SimpleFeature feature = iterator.next(); ... } } finally { iterator.close(); }
JTSFactory¶
We are cutting down on “anonymous” FactoryFinder use; creating JTSFactory to allow the
entire GeoTools library to share a JTS GeometryFactory.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.4 code):
GeometryFactory factory = new FactoryFinder().getGeometryFactory( null );
AFTER (GeoTools 2.5 code):
GeometryFactory factory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory( null );
ProgressListener¶
Transition to gt-opengis ProgressListener.
Before (GeoTools 2.2 Code):
progress.setDescription( message );
After (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
progress.setTask( new SimpleInternationalString( message ) );
To upgrade:
Search:
import org.geotools.util.ProgressListenerReplace:
import org.opengis.util.ProgressListenerUpdate:
setTask( new SimpleInternationalString( message ) ); // was setDescription( message );
SimpleFeature¶
We have (finally) made the move to an improved feature model. Please take the opportunity
to change your existing code to use org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeature. The existing
GeoTools Feature interface is still in use; but it has been updated in
place to extend SimpleFeature.
Before (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
import org.geotools.feature.FeatureType; ... CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = CRS.decode("EPSG:4326"); final AttributeType GEOM = AttributeTypeFactory.newAttributeType("Location",Point.class,true, null,null,crs ); final AttributeType NAME = AttributeTypeFactory.newAttributeType("Name",String.class, true ); final FeatureType FLAG = FeatureTypeFactory.newFeatureType(new AttributeType[] { GEOM, NAME },"Flag"); Feature flag1 = FLAG.create( "flag.1", new Object[]{ point, "Here" } ); AttributeType attributes[] = FLAG.getAttributeTypes(); AttributeType location = FLAG.getAttribute("Location"); String label = location.getName(); Class binding = location.getType(); Geometry geom = flag1.getDefaultGeometry();
After (GeoTools 2.5 Code):
import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType; ... SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder builder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder(); builder.setName( "Flag" ); builder.setNamespaceURI( "http://localhost/" ); builder.setCRS( "EPSG:4326" ); builder.add( "Location", Point.class ); builder.add( "Name", String.class ); SimpleFeatureType FLAG = builder.buildFeatureType(); SimpleFeature flag1 = SimpleFeatureBuilder.build( FLAG, new Object[]{ point, "Here"}, "flag.1" ); List<AttributeDescriptor> attributes = FLAG.getAttributes(); AttributeDescriptor location = FLAG.getAttribute("Location"); String label = location.getLocationName(); Class binding = location.getType().getBinding(); Geometry geom = (Geometry) flag1.getDefaultGeometry();
Here are some steps to start you off updating your code:
Search Replace
Search:
Featurereplace withSimpleFeatureSearch:
FeatureTypereplace withSimpleFeatureType
Fix the imports
Control-Shift-O in Eclipse IDE
Add casts as required for
getDefaultGeometry()
FeatureType.createhas been replaced withSimpleFeatureBuilderThere is a static method to make the transition easier:
SimpleFeatureFeatureBuilder.build( schema, attributes, fid );
For more code examples please see:
AttributeDescriptor and AttributeType¶
The concept of an AttributeType has been split into two now (allowing you to reuse common types).
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
import org.geotools.feature.AttributeType; ... GeometryAttributeType att = (GeometryAttributeType) AttributeTypeBuilder.newAttributeDescriptor(geomTypeName, targetGeomType, isNillable, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Collections.EMPTY_LIST, crs );
AFTER (GeoTools 2.5 Code):
import org.geotools.feature.AttributeTypeBuilder; import org.opengis.feature.type.AttributeDescriptor ... AttributeTypeBuilder build = new AttributeTypeBuilder(); build.setName( geomTypeName ); build.setBinding( targetGeomType ); build.setNillable(true); build.setCRS(crs); GeometryType type = build.buildGeometryType(); GeometryDescriptor attribute = build.buildDescriptor( geomTypeName, type );
Name¶
In order to better support app-schema work we can no longer assume names are a simple String. The
Name class has been introduced to make this easier and is available
throughout the library: example FeatureSource.getName().
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
DataStore ds = ... String []typeNames = ds.getTypeNames(); SimpleFeatureType type = ds.getSchema(typeNames[0]); assert type.getTypeName() == typeNames[0]; FeatureSource source = ds.getFeatureSource(type.getTypeName());
AFTER (GeoTools 2.5 Code):
import org.opengis.feature.type.Name; ... DataStore ds = ... List<Name> featureNames = ds.getNames(); SimpleFeatureType type = ds.getSchema(featureNames.get(0)); // type.getName() may or may not be equal to featureNames.get(0), assume not. If they're its just an implementation detail. FeatureSource source = ds.getFeatureSource(featureNames.get(0));
DataStore¶
Transition to use of Java 5 Generics with DataStore API.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
DataStore ds = ... FeatureSource source = ds.getSource(typeName); FeatureStore store = (FeatureStore)source; FeatureLocking locking = (FeatureLocking)source; FeatureCollection collection = source.getFeatures(); FeatureIterator features = collection.features(); while(features.hasNext){ SimpleFeature feature = features.next(); } Transaction transaction = Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT; FeatureReader reader = ds.getFeatureReader(new DefaultQuery(typeName), transaction); FeatureWriter writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(typeName, transaction);
AFTER (GeoTools 2.5 Code):
DataStore ds = ... FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> source = ds.getSource(typeName); FeatureStore<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> store = (FeatureStore<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>)source; FeatureLocking<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> locking = (FeatureLocking<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature>)source; FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> collection = source.getFeatures(); FeatureIterator<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> features = collection.features(); while(features.hasNext){ SimpleFeature feature = features.next(); } Transaction transaction = Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT; FeatureReader<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> reader = ds.getFeatureReader(new DefaultQuery(typeName), transaction); FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(typeName, transaction);
AFTER (GeoTools 2.7 Code):
DataStore ds = ... SimpleFeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> source = ds.getSource(typeName); SimpleFeatureStore store = (SimpleFeatureStore) source; SimpleFeatureLocking locking = (SimpleFeatureLocking) source; SimpleFeatureCollection collection = source.getFeatures(); SimpleFeatureIterator features = collection.features(); while(features.hasNext){ SimpleFeature feature = features.next(); } Transaction transaction = Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT; FeatureReader<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> reader = ds.getFeatureReader(new DefaultQuery(typeName), transaction); FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType,SimpleFeature> writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(typeName, transaction);
DataAccess and DataStore¶
The
DataAccesssuper class has been introduced, leaving DataStore to only work withSimpleFeaturecapable implementations.:import org.opengis.feature.type.Name; ... java.util.Map paramsMap = ... DataStore ds = DataStoreFinder.getDataStore(paramsMap); Name featureName = new org.geotools.feature.Name(namespace, localName); FeatureSource<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> source = ds.getSource(featureName); FeatureStore<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> store = (FeatureStore)source; FeatureLocking<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> locking = (FeatureLocking)source; FeatureCollection<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> collection = source.getFeatures(); FeatureIterator<SimpleFeature> features = collection.features(); while(features.hasNext){ SimpleFeature feature = features.next(); } Transaction transaction = Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT; FeatureReader<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> reader = ds.getFeatureReader(new DefaultQuery(typeName), transaction); FeatureWriter<SimpleFeatureType, SimpleFeature> writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(typeName, transaction);
DataAccess: works both withSimpleFeatureand normalFeaturecapable implementations:import org.opengis.feature.FeatureType; import org.opengis.feature.Feature; import org.opengis.feature.type.Name; ... java.util.Map paramsMap = ... DataAccess<FeatureType, Feature> ds = DataAccessFinder.getDataAccess(paramsMap); Name featureName = new org.geotools.feature.Name(namespace, localName); FeatureSource<FeatureType, Feature> source = ds.getSource(featureName); FeatureStore<FeatureType, Feature> store = (FeatureStore)source; FeatureLocking<FeatureType, Feature> locking = (FeatureLocking)source; FeatureCollection<FeatureType, Feature> collection = source.getFeatures(); FeatureIterator<Feature> features = collection.features(); while(features.hasNext){ Feature feature = features.next(); } //No DataAccess.getFeatureReader/Writer
GeoTools 2.4¶
The GeoTools 2.4.0 release is a major change to the GeoTools library due to the adoption of GeoAPI
Filter model. This new filter model is immutable making it impossible to modify filters that
have already been constructed; in trade it is thread safe.
The following is needed when upgrading to 2.4.
ReferencingFactoryFinder¶
Rename FactoryFinder to ReferencingFactoryFinder
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.2 Code):
CRSFactory factory = FactoryFinder.getCSFactory( null );
AFTER (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
CRSFactory factory = ReferencingFactoryFinder.getCSFactory( null );
FeatureStore addFeatures¶
The use of FeatureReader has been removed from the FeatureStore API.
Before (GeoTools 2.2 Code):
featureStore.addFeatures( DataUtilities.reader( collection )); // add FeatureCollection featureStore.addFeatures( DataUtilities.reader(array)); // add Feature[] featureStore.addFeatures( DataUtilities.reader(feature )); // add Feature featureStore.addFeatures( reader );
After (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
featureStore.addFeatures( collection ); // add FeatureCollection featureStore.addFeatures( DataUtilities.collection( array ) ); // add Feature[] featureStore.addFeatures( DataUtilities.collection( feature )); // add Feature featureStore.addFeatures( DataUtilities.collection( reader )); // add FeatureReader
Note:
DataUtilities.collection(reader)will currently load the contents into memory, if you have any volunteer time a “lazy” implementation would be helpful.
FeatureSource getSupportedHints¶
We added a getSupportedHints() method that can be used to check which Query hints are supported
by a certain FeatureSource. If your FeatureSource does not intend to leverage query hints, just
return an empty set.
After (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
/** * By default, no Hints are supported */ public Set getSupportedHints() { return Collections.EMPTY_SET; }
Query getHints¶
We have added the method Query.getHints() allow users to pass in hints to control the query
process.
If you have a Query implementation other than DefaultQuery you’ll need to add the getHints() method.
The default implementation, if you don’t plan to leverage hints, can just return an
empty Hints object.
After (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
/** * Returns an empty Hints set */ public Hints getHints() { return new Hints(Collections.emptyMap()); }
Filter¶
We have completed the transition to GeoAPI Filter.
Before (GeoTools 2.2 Code):
package org.geotools.filter; import junit.framework.TestCase; import org.geotools.filter.LogicFilter; import org.geotools.filter.FilterFactory; import org.geotools.filter.Filter; public class FilterFactoryBeforeTest extends TestCase { public void testBefore() throws Exception { FilterFactory ff = FilterFactoryFinder.createFilterFactory(); CompareFilter filter = ff.createCompareFilter(Filter.COMPARE_GREATER_THAN); filter.addLeftValue( ff.createLiteralExpression(2)); filter.addRightValue( ff.createLiteralExpression(1)); assertTrue( filter.contrains( null ) ); assertTrue( filter.getFilterType() == FilterType.COMPARE_GREATER_THAN ); assertTrue( Filter.NONE != filter ); } }
AFTER (Quick GeoTools 2.3 Code):
public void testQuick() throws Exception { FilterFactory ff = FilterFactoryFinder.createFilterFactory(); CompareFilter filter = ff.createCompareFilter(FilterType.COMPARE_GREATER_THAN); filter.addLeftValue( ff.createLiteralExpression(2)); filter.addRightValue( ff.createLiteralExpression(1)); assertTrue( filter.evaluate( null ) ); assertTrue( Filters.getFilterType( filter ) == FilterType.COMPARE_GREATER_THAN); assertTrue( Filter.INCLUDE != filter ); }
Here are the steps to follow to update your own code:
Substitute.
Search
Replace
import org.geotools.filter.Filter;import org.opengis.filter.Filter;import org.geotools.filter.SortBy;import org.opengis.filter.sort.SortBy;Filter.NONEFilter.INCLUDEFilter.ALLFilter.EXCLUDEAbstractFilter.COMPAREFilterType.COMPAREFilter.COMPAREFilterType.COMPAREFilter.GEOMETRYFilterType.GEOMETRYFilter.LOGICFilterType.LOGICFilterypeis no longer supported directly.BEFORE:
int type = filter.getFilterType();
AFTER:
int type = Filters.getFilterType( filter );
You can no longer chain filters together.
BEFORE:
filter = filter.and( other )
AFTER:
filter = filterFactory.and( filter, other );
We have provided an adapter for your old filter visitors.
BEFORE:
filter.accept( visitor )
AFTER:
Filters.accept( filter, visitor );
Update your code to use the new factory methods.
BEFORE:
filter = filterFactory.createCompareFilter(FilterType.COMPARE_EQUALS) filter.setLeftGeometry( expr1 ); filter.setRightGeometry( expr3 );
AFTER:
filter = FilterFactory.equals(expr1,expr);
Literals cannot be modified once created.
BEFORE:
Literal literal = filterFactory.createLiteral(); literal.setLiteral( obj );
AFTER:
Filter filter = filterFactory.literal( obj );
Property name support.
BEFORE:
filter = = filterFac.createAttributeExpression(schema, "name");
AFTER:
Filter filter = filterFactory.property(name);
After (GeoTools 2.4 Code):
public void testAfter() throws Exception {
FilterFactory ff = CommonFactoryFinder.getFilterFactory(null);
Expression left = ff.literal(2);
Expression right = ff.literal(2);
PropertyIsGreaterThan filter = ff.greater( left, right );
assertTrue( filter.evaluate( null ) );
assertTrue( Filter.INCLUDE != filter );
}
Substitute
Search
Replace
import org.geotools.filter.FilterFactory;import org.opengis.filter.FilterFactory;FilterFactoryFinder.createFilterFactory()CommonFactoryFinder.getFilterFactory(null);import org.geotools.filter.FilterFactoryFinder;import org.geotools.factory.CommonFactoryFinderimport org.geotools.filter.CompareFilter;import org.geoapi.spatial.BinaryComparisonOperatorCompareFilterBinaryComparisonOperatorUpdate code to use evaluate.
BEFORE:
if( filter.contains( feature ){
AFTER:
if( filter.evaluate( feature ){
Update code to use
instanceofchecks.BEFORE:
if( filter.getFilterType() == FilterType.GEOMETRY_CONTAIN ) {
AFTER:
if( filter instanceof Contains ){
Note regarding different Geometries
GeoTools was formally limited to only JTS Geometry
GeoTools filter now can take either JTS Geometry or ISO Geometry
If you need to convert from one to the other:
JTSUtils.jtsToGo1(p, CRS.decode("EPSG:4326"));
Feature.getParent removed¶
The feature.getParent() method have been deprecated as a mistake and has now been removed.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.0 Code):
public void example( FeatureSource source ){ FeatureCollection features = source.getFeatures(); Iterator i = features.iterator(); try { while( i.hasNext() ){ Feature feature = (Feature) i.next(); System.out.println( precentBoxed( feature )); } } finally { features.close( i ); } } private double precentBoxed( Feature feature ){ Envelope context = feature.getParent().getBounds(); Envelope bbox = feature.getBounds(); double boxedContext = context.width * context.height; double boxed = bbox.width * bbox.height; return (boxed / boxedContext) * 100.0 }
AFTER (GeoTools 2.2 Code):
public void example( FeatureSource source ){ FeatureCollection features = source.getFeatures(); Iterator i = features.iterator(); try { while( i.hasNext() ){ Feature feature = (Feature) i.next(); System.out.println( precentBoxed( feature, features )); } } finally { features.close( i ); } } private double precentBoxed( Feature feature, FeatureCollection parent ){ Envelope context = parent.getBounds(); Envelope bbox = feature.getBounds(); double boxedContext = context.width * context.height; double boxed = bbox.width * bbox.height; return (boxed / boxedContext) * 100.0 }
Notes:
you will have to make API changes to pass the intended parent collection in
This is a mistake with the previous feature model (for a feature can exist in more then one collection) and we apologize for the inconvenience.
Split Classification Expressions
The biggest user of the feature.getParent() mistake was the implementation of classification
functions. You will now need to split up these expressions into two parts.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.3):
equal_interval( SPEED, 12 )uses
getParent()internally to produce classification on feature collection;then checks which category each feature falls into
Notes:
please note the above code depends on
getParent()so it is not safe even for GeoTools 2.3 (as some features have a null parent).
AFTER (GeoTools 2.4):
Apply the aggregation function to the feature collection:
equalInterval( SPEED, 12 )produce classification on provided feature collection
Construct a slot expression using the resulting literal:
classify( SPEED, {0} )
use literal classification from step one
GTRenderer¶
The GTRender interface was produced as a neutral ground for client code; traditional users of
LiteRenderer and LiteRenderer2 are asked to move to the implementation of GTRenderer called
StreamingRenderer.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.1):
How to paint to an outputArea Rectangle:
LiteRenderer2 draw = new LiteRenderer2(map); Envelope dataArea = map.getLayerBounds(); AffineTransform transform = renderer.worldToScreenTransform(dataArea, outputArea); draw.paint(g2d, outputArea, transform);
QUICK (GeoTools 2.2)
How to paint to an outputArea Rectangle:
StreamingRenderer draw = new StreamingRenderer(); draw.setContext(map); draw.paint(g2d, outputArea, map.getLayerBounds() );
BEST PRACTICE (GeoTools 2.2):
GTRenderer draw = new StreamingRenderer(); draw.setContext(map); draw.paint(g2d, outputArea, map.getLayerBounds() );
By letting your code depend only on the
GTRendererinterface you can experiment with alternative implementations to find the best fit.
JTS¶
Swap moved to JTS utility class.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.1):
import org.geotools.geometry.JTS; import org.geotools.geometry.JTS.ReferencedEnvelope
AFTER (GeoTools 2.2):
import org.geotools.geometry.jts.JTS; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.ReferencedEnvelope
JTS to Shape converters¶
Swap to moved Renderer JTS-to-Shape converters.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.3):
import org.geotools.renderer.lite.LiteShape; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.LiteShape2; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.PackedLineIterator; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.PointIterator; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.PolygonIterator; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.LineIterator; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.LineIterator2; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.Decimator; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.AbstractLiteIterator; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.TransformedShape; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.LiteCoordinateSequence; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.LiteCoordinateSequenceFactory; import org.geotools.renderer.lite.LiteCoordinateSequence;
AFTER (GeoTools 2.4):
import org.geotools.geometry.jts.LiteShape; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.LiteShape2; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.PackedLineIterator; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.PointIterator; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.PolygonIterator; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.LineIterator; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.LineIterator2; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.Decimator; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.AbstractLiteIterator; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.TransformedShape; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.LiteCoordinateSequence; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.LiteCoordinateSequenceFactory; import org.geotools.geometry.jts.LiteCoordinateSequence;
Coverage utility classes¶
Swap to moved Coverage utility classes.
BEFORE (GeoTools 2.3):
import org.geotools.data.coverage.grid.* import org.geotools.image.imageio.*
Wrapping a
GridCoverageinto a feature in 2.3:org.geotools.data.DataUtilities#wrapGc(GridCoverage gridCoverage) org.geotools.data.DataUtilities#wrapGcReader( AbstractGridCoverage2DReader gridCoverageReader, GeneralParameterValue[] params)
GridCoverageExchangeUtility classes in 2.3:org.geotools.data.coverage.grid.file.* org.geotools.data.coverage.grid.stream .*
org.geotools.coverage.ioclasses in 2.3:org.geotools.coverage.io.AbstractGridCoverageReader.java, org.geotools.coverage.io.AmbiguousMetadataException.java, org.geotools.coverage.io.ExoreferencedGridCoverageReader.java, org.geotools.coverage.io.MetadataBuilder.java, org.geotools.coverage.io.MetadataException.java, org.geotools.coverage.io.MissingMetadataException.java
AFTER (GeoTools 2.4):
import org.geotools.coverage.grid.io.* import org.geotools.coverage.grid.io.imageio.*
Wrapping a
GridCoverageinto a feature in 2.4:org.geotools.referencing.util.coverage.CoverageUtilities #wrapGc(GridCoverage gridCoverage) org.geotools.referencing.util.coverage.CoverageUtilities #wrapGcReader( AbstractGridCoverage2DReader gridCoverageReader, GeneralParameterValue[] params)
GridCoverageExchangeUtility classes in 2.4.The classes have been dismissed since apparently nobody was using. If needed we can reintroduce them as deprecated.
org.geotools.coverage.ioclasses in 2.4.These classes have been moved to
spike/exoreferencedwaiting for Martin to review and merge intoorg.geotools.coverage.grid.iopackage
spatialschema¶
Renamed spatialschema to geometry.
Do you know what
spatialschemawas? We did not find it clear either.Renamed to
geometry?BEFORE:
import org.opengis.spatialschema.geometry; import org.opengis.spatialschema.geometry.aggregate; import org.opengis.spatialschema.geometry.complex; import org.opengis.spatialschema.geometry.geometry; import org.opengis.spatialschema.geometry.primitive;
AFTER:
import org.opengis.geometry; import org.opengis.geometry.aggregate; import org.opengis.geometry.complex; import org.opengis.geometry.coordinate; import org.opengis.geometry.primitive;
World Image¶
Sets of World Image extensions. Changed from a single String to a
Set<String> .. because
one wld is not enough?
BEFORE:
private File toWorldFile(String fileRoot, String fileExt){ File worldFile = new File( fileRoot + ".wld" ); if( worldFile.exists() ){ return worldFile; } String ext = WorldImageFormat.getWorldExtension( fileExt ); File otherWorldFile = new File( fileRoot + ext ); if( otherWorldFile.exists() ){ return otherWorldFile; } return null; }
AFTER:
private File toWorldFile(String fileRoot, String fileExt){ Set<String> other = WorldImageFormat.getWorldExtension( fileExt ); File worldFile = new File( fileRoot + ".wld" ); if( worldFile.exists() ){ return worldFile; } for( String ext : other ){ File otherWorldFile = new File( fileRoot + ext ); if( otherWorldFile.exists() ){ return otherWorldFile; } } return null; }