Envelope¶
GeoTools supports working with JTS Topology Suite Envelopes (used to represent the extent of a Geometry).
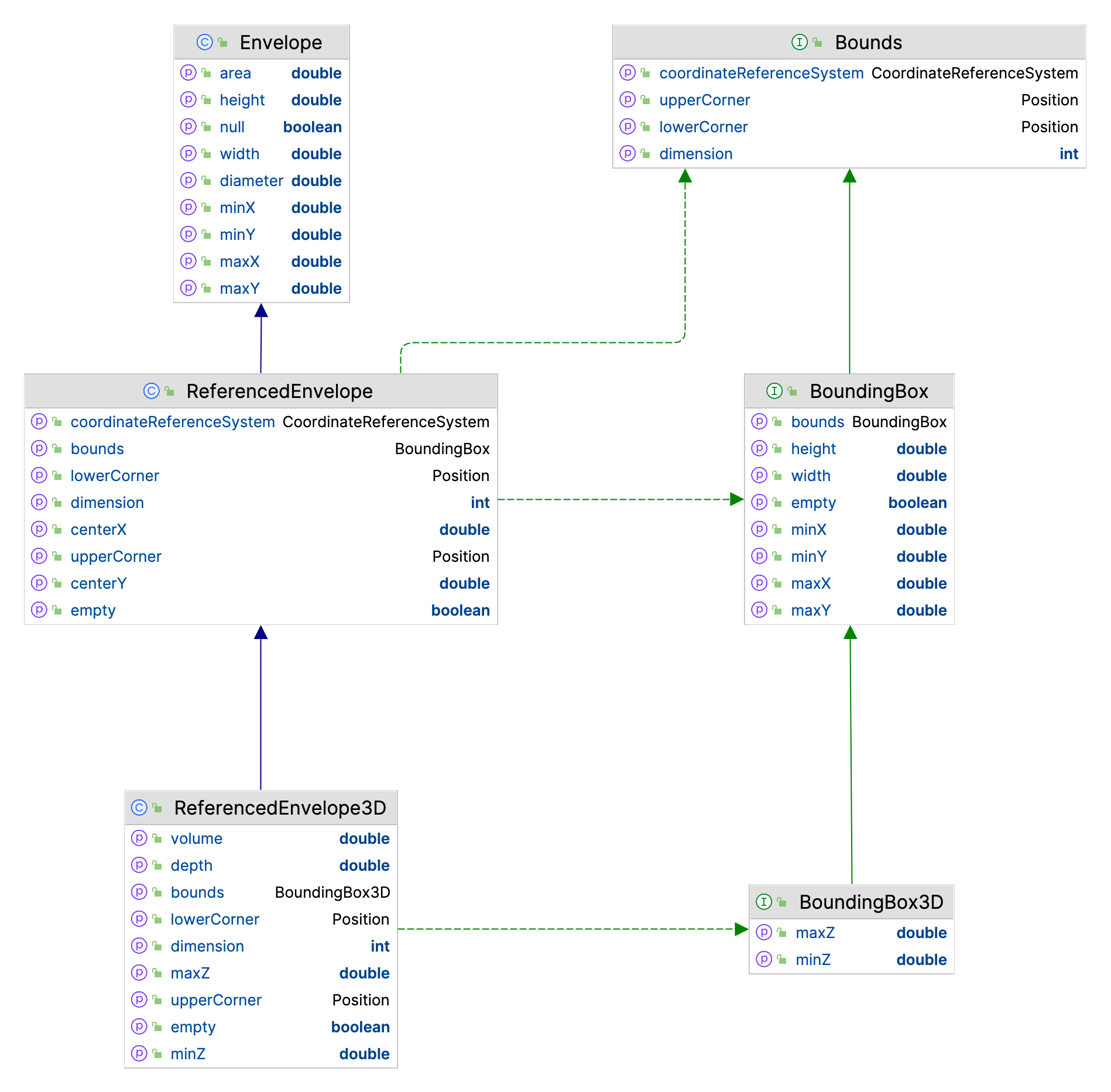
The git-main module defines ReferencedEnvelope and ReferencedEnvelope3D as an integration between JTS Geometry model and gt-api Bounds and Bound3D interfaces.
JTS Envelope¶
The JTS Topology Suite has the concept of an Envelope recorded in x1,x2, y1,y2 order.
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Envelope envelope = new Envelope(0, 10, 0, 20);
double xMin = envelope.getMinX();
double yMin = envelope.getMinY();
double xMax = envelope.getMaxX();
double yMax = envelope.getMaxY();
double width = envelope.getWidth(); // assuming axis 0 is easting
double height = envelope.getHeight(); // assuming axis 1 is nothing
// Expand an existing envelope
Envelope bbox = new Envelope();
envelope.expandToInclude(bbox);
// Use
envelope.covers(5, 10); // inside or on edge!
envelope.contains(5, 10); // inside only
// Null
envelope.isNull(); // check if "null" (not storing anything)
envelope.setToNull();
Envelope Transform¶
Transform an Envelope using the JTS Utility class:
CoordinateReferenceSystem sourceCRS = CRS.decode("EPSG:4326");
CoordinateReferenceSystem targetCRS = CRS.decode("EPSG:23032");
Envelope envelope = new Envelope(0, 10, 0, 20);
MathTransform transform = CRS.findMathTransform(sourceCRS, targetCRS);
Envelope quick = JTS.transform(envelope, transform);
// Sample 10 points around the envelope
Envelope better = JTS.transform(envelope, null, transform, 10);
ReferencedEnvelope¶
GeoTools ReferencedEnvelope extends JTS Envelope to implement the gt-api module Bounds interface.
ReferencedEnvelope is all of these:
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Envelope- as defined by the JTS Topology System ( a Simple Feature for SQL concept)org.geotools.api.geometry.BoundingBox- 2D bounds as defined by the ISO 19107 Geometryorg.geotools.api.geometry.Bounds- captures 3D bounds as defined by ISO 19107 Geometry.
To support 3D bounds (and use a 3D Coordinate Reference System) we must create an instance of the child class ReferencedEnvelope3D (see below).
Use of ReferencedEnvelope is the most common representation of a bounds in GeoTools. The constructor expects the extent to be defined in xMin,xMax,yMin,yMax order for a 2D CoordianteReferenceSystem:
ReferencedEnvelope envelope = new ReferencedEnvelope(0, 10, 0, 20, DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84);
double xMin = envelope.getMinX();
double yMin = envelope.getMinY();
double xMax = envelope.getMaxX();
double yMax = envelope.getMaxY();
double width = envelope.getWidth();
double height = envelope.getHeight();
double xCenter = envelope.getMedian(0);
double yCenter = envelope.getMedian(1);
CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = envelope.getCoordinateReferenceSystem();
int dimension = envelope.getDimension();
// Direct access to internal upper and lower positions
Position lower = envelope.getLowerCorner();
Position upper = envelope.getUpperCorner();
// expand to include 15, 30
envelope.include(15, 30);
envelope.isEmpty(); // check if storing width and height are 0
envelope.isNull(); // check if "null" (not storing anything)
envelope.setToNull();
ReferencedEnvelope Transform¶
ReferencedEnvelope does one thing very well; it is an JTS Envelope that has a CoordinateReferenceSystem. Using this CoordinateReferenceSystem you can quickly transform it between projections.:
CoordinateReferenceSystem sourceCRS = CRS.decode("EPSG:4326");
ReferencedEnvelope envelope = new ReferencedEnvelope(0, 10, 0, 20, sourceCRS);
// Transform using 10 sample points around the envelope
CoordinateReferenceSystem targetCRS = CRS.decode("EPSG:23032");
ReferencedEnvelope result = envelope.transform(targetCRS, true, 10);
ReferencedEnvelope is used in a lot of GeoTools interfaces to represent the requirement to have a CoordianteReferenceSystem.
Using a raw JTS Envelope without knowing the CoordinateReferenceSystem presents difficulty -
due to incomplete information client code is forced to make an assumption. Some code may assumes
the envelope is in WGS84 while other code may assumes it is in the same “native” CoordinateReferenceSystem as
the data being worked on.
When working with older code examples, you may need to read the javadocs to determine another method to used
to define the CoordinateReferenceSystem for a returned Envelope.
Using a
FeatureSourcewithoutReferencedEnvelopeexample:Envelope bounds = featureSource.getBounds(); CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = featureSource.getSchema().getDefaultGeometry().getCoordinateSystem();
Using a
FeatureSourcewithReferencedEnvelope:ReferencedEnvelope bounds = (ReferencedEnvelope) featureSource.getBounds(); CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = bounds.getCoordinateReferenceSystem();
ReferencedEnvelope3D¶
GeoTools ReferencedEnvelope3D extends JTS Envelope to implement the gt-api module Bounds3D interface.
ReferencedEnvelope3D is all of these:
ReferencedEnvelopeincluding all parent classes and interfacesorg.geotools.api.geometry.BoundingBox3D- 3D bounds as defined by the ISO 19107 Geometry
This is the class to use when you want to represent a 3D bounds in GeoTools. The constructor expects the input in xMin,xMax,yMin,yMax,zMin,zMax order and expects a 3D CRS:
ReferencedEnvelope3D envelope = new ReferencedEnvelope3D(0, 10, 0, 20, 0, 30, DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84_3D);
double xMin = envelope.getMinX();
double yMin = envelope.getMinY();
double zMin = envelope.getMinZ();
double xMax = envelope.getMaxX();
double yMax = envelope.getMaxY();
double zMax = envelope.getMaxZ();
double width = envelope.getWidth();
double height = envelope.getHeight();
double depth = envelope.getDepth();
double xCenter = envelope.getMedian(0);
double yCenter = envelope.getMedian(1);
double zCenter = envelope.getMedian(2);
CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = envelope.getCoordinateReferenceSystem();
int dimension = envelope.getDimension();
// Direct access to internal upper and lower positions
Position lower = envelope.getLowerCorner();
Position upper = envelope.getUpperCorner();
// expand to include 15, 30, 40
envelope.include(15, 30, 40);
envelope.isEmpty(); // check if storing width and height are 0
envelope.isNull(); // check if "null" (not storing anything)
envelope.setToNull();
ReferencedEnvelope utility methods¶
When using a 3D CoordinateReferenceSystem we must create an instance of ReferencedEnvelope3D and not of its parent ReferencedEnvelope class.
If we are not sure what dimension we are dealing with, there are safe ways to create, copy, convert or reference ReferencedEnvelope instances:
create()methods: safely create a new ReferencedEnvelope instance (always makes a copy)rect()methods: safely create from a java.awtRectangleenvelope()methods: safely create from a jtsEnvelopereference()methods: safely “cast” an existing object toReferencedEnvelope(only making a copy if needed)
Example use of ReferencedEnvelope utility methods:
// can hold both regular ReferencedEnvelope as well as ReferencedEnvelope3D
ReferencedEnvelope env;
// can be instance of ReferencedEnvelope3D;
ReferencedEnvelope original = null;
// can be 2D or 3D
CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = null;
// can be instance of ReferencedEnvelope(3D)
Bounds opengis_env = null;
// can be instance of ReferencedEnvelope(3D)
org.locationtech.jts.geom.Envelope jts_env = null;
// can be instance of ReferencedEnvelope or ReferencedEnvelope3D
BoundingBox bbox = null;
// safely copy ReferencedEnvelope, uses type of original to determine type
env = ReferencedEnvelope.create(original);
// safely create ReferencedEnvelope from CRS, uses dimension to determine type
env = ReferencedEnvelope.create(crs);
// safely create ReferencedEnvelope from org.geotools.api.geometry.Envelope,
// uses dimension in Envelope to determine type
env = ReferencedEnvelope.create(opengis_env, crs);
// safely create ReferencedEnvelope from org.locationtech.jts.geom.Envelope,
// uses dimension in Envelope to determine type
env = ReferencedEnvelope.envelope(jts_env, crs);
// safely reference org.geotools.api.geometry.Envelope as ReferencedEnvelope
// --> if it is a ReferencedEnvelope(3D), simply cast it; if not, create a conversion
env = ReferencedEnvelope.reference(opengis_env);
// safely reference org.locationtech.jts.geom.Envelope as ReferencedEnvelope
// --> if it is a ReferencedEnvelope(3D), simply cast it; if not, create a conversion
env = ReferencedEnvelope.reference(jts_env);
// safely reference BoundingBox as ReferencedEnvelope
// --> if it is a ReferencedEnvelope(3D), simply cast it; if not, create a conversion
env = ReferencedEnvelope.reference(bbox);