Package org.geotools.data.complex
This package contains the implementation of a ComplexDataStore,
Author note: though this "Complex" datastore has born to provide
complex features out of a simple features data source, it may be better
called a DerivativeDataStore or something like that, you'll see
why later.
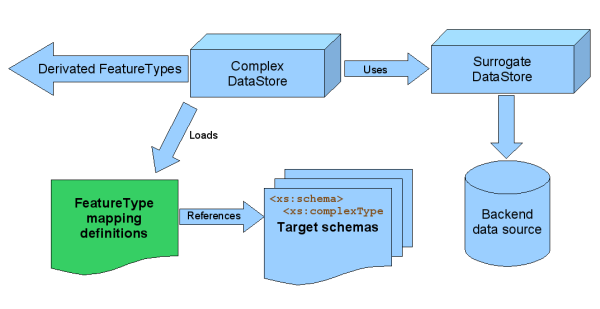
This DataStore implementation acts as a wrapper over one or more
DataStores, from now on, the surrogate DataStores, and allows to
specify a series of mappings between the properties of surrogate
FeatureTypes and output schemas. This mappings, in turn, allows to
specify properties of the target FeatureTypes as being derivated by the
evaluation of an org.geotools.filter.Expression defined
against the surrogate FeautreType.
So, what is this useful for? Suppose you have a database of feature types you need to serve out of your office or organization. Furthermore, suppose you need to serve that data in an externally defined schema (like one defined by INSPIRE or any other organization). Obviously you don't want to rearchitect your database to conform to that schema! And indeed you probably even can't do that without the assistance of some kind of object-relational mapping layer. Now you can better figure out what this ComplexDataStore is about if you think on it as a kind of object-relational mapping layer, but targeted to GIS data. Though not exact, this pseudo definition can help you understand it if its your first time reading this document.
Of course it has nothing to do with relational databases directly, but with mapping an existing GeoTools FeatureType from your internal storage schema to an externally defined one, which we're getting used to call "community schemas".
How does ComplexDataStore achieves that?
You need:
- An output (community) schema. This schema exists independently of your actual data structures, so it will be loaded from a GML schema file, defined in XML Schema language.
- An input FeatureType. GeoTools FeatureTypes are exposed by GeoTools DataStores, so you need a way to specify the DataStore's connection parameters and the source FeatureType name.
- The attribute and attribute id mapping definitions. They consists of a series of couples of XPath and OGC Filter 1.0 Expressions. The former addresses the output schema properties and the later defines how the value of that properties are derived from the source Feature instances.
To persist this information, use a XML file which contains this definitions, and whose location in the form of an URL must be used to create a DataStore instance through the GeoTools DataStoreFinder lookup system.
-
ClassDescriptionBase class for several MappingFeatureImplementation's.A
DataAccessthat maps a "simple" sourceDataStoreinto a source of full Feature features conforming to an application schema.DataStoreFactory for ComplexDataStore.A registry that stores all app schema data access instances per application.A Collection of AttributeMappings that correspond to complex types that need to be created.A Feature iterator that operates over the FeatureSource of a FeatureTypeMapping and produces Features of the output schema by applying the mapping rules to the Features of the source schema.A registry that stores data access instances per application.Base class for Indexed IteratorsFactory for IndexedMappingFeatureIterator subclassesIterator for result ids from index datasourceIndex iterator for to work with a FeatureIterator delegateIndex iterator for to work with UniqueVisitor over id field.Manages unrolled Query indexes and partial indexesPartial Indexed Query management/transform/utilsA Feature iterator that operates over the FeatureSource of a FeatureTypeMapping that is of a simple content type, e.g. representing a gml:name element.FeatureCollectionfor aMappingFeatureIterator.A FeatureSource that uses a FeatureTypeMapping to perform Feature fetching.This class represents AttributeMapping for attributes that are nested inside another complex attribute.MappingFeatureIterator with partial index query supportAn extension to DataAccessMappingFeatureIterator where filter is present.MappingFeatureIterator for full index coverage caseAn implementation of AbstractMappingFeatureIterator to handle XML datasources.